The wars of Portugal and Spain ( 1808-1814 ) Machine
translation
The overthrow of Napoleon
Having concludes to
Tilsitt a temporary peace
with the Czar of Russia, the Emperor had become allied with king of
Spain Charles IV to establish(constitute) a French-Spanish
expeditionary force which went to occupy Portugal ally of England.
Under excuse to strengthen his troops of activity(occupation), Napoleon
made an overthrow against Spanish garrisons then forced king of Spain
to the abdication for the benefit of his brother Joseph Napoleon. In
front of these actions, the population from Madrid rebelled on May 8th,
1808, at the beginning of the fight of Spanish liberation against the
French troops.
This situation provokes the desertion of the Spanish contingent under
command of the general Junot with which the troops are harassed from
July by a Portuguese insurection bound(connected) to the Spanish
troops. July 21st, 1808, general Dupont of the Estang capitulates at a
Spanish army, to Bailen, in Spain while he went to the south of
Portugal. Then on August 1st, an English expeditionary force
commanded(ordered) by Sir Arthur Wellesley, the future duke of
Wellington, lands in Portugal to support Portuguese and
gathered(reunited) Spanish.
In front of this local military coalition, the French troops are beaten
first time to Evora then one second on August 21st, 1808 to Vimeiro.
His(her) decimated army, Junot has to capitulate and signs in Arched an
agreement with the English which allows him(her) to return by sea its
troops deprived of materials to Rochefort and Quiberon. From this
double surrender, Portugal will act as back base for the English army
provided by its fleet.
Napoleon increases the
number of pontonniers
From April and to be close
to military actions engaged(opened), the Emperor had settled down in
Bayonne and visited on Thursday, April 21st, 1808 the
deposit(warehouse) of the military materials of this city. He(it) found
the material there - pontoons and easels built in 1794, for the
pontonniers of the army of Western Pyrenees and apparently not used.
He(it) made recondition this material (Conference of Jean-Claude
Lorblanches for the Napoleonic Recollection) and gave the following
order kept(preserved) in the minutes of Secrétairerie of
State
dated July 13th, 1808 1 in Bayonne. « The 1st battalion of
pontonniers will henceforth consist of 10 companies. 2 ème
will
consist of 6 companies ". Following this decree, 2nd and 5th companies
of the 2nd battalion which were in Austria pass to the 1st battalion
following 8 affected companies. They take the naming of 9
ème
and 10 ème companies.
Creation of the army of
Spain and affectation(appointment) of
pontonniers.
Then Napoleon created on September 7th, 1808 the army of
Spain, which contained the already spot troops, with as additional help
the 1st armed force of the marshal Victor come directly from the army
of the Rhine, with 6 ème company of pontonniers and its
material, which was incorporated into him(her).
So at the beginning of October, 1808, 180.000 foot soldiers,
artillerymen and gunners subdivided into 6 armed forces parked in
Spain.
The companies of pontonniers arrived to Bayonne in the course of
October, via Strasbourg where their workforce had been completed. It
was a question 2 ème and 4 ème company of the 1st
battalion comings without material of passage of river, their
individual armaments and 5 horses. From their arrival they joined the
armed force to whom(which) they were allocated.
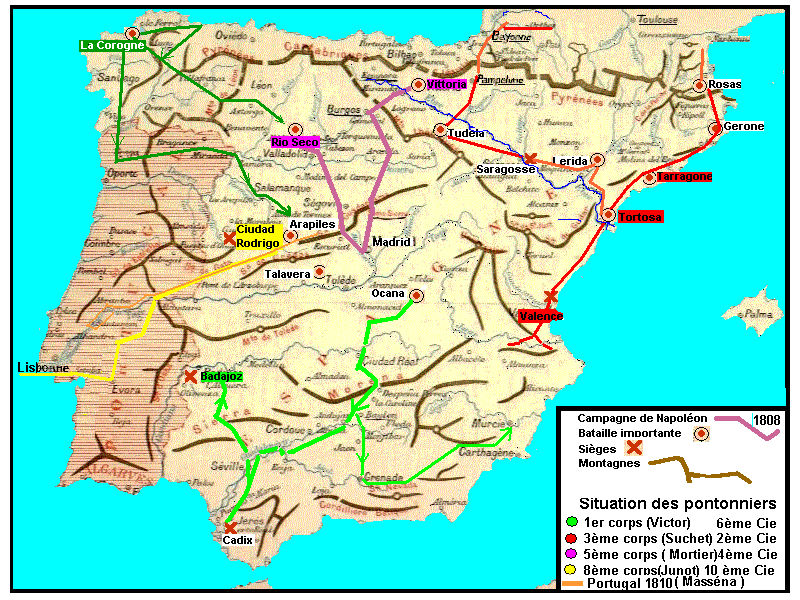
So from October 1808, the 1st battalion of pontonniers included the
following companies which will stay in Spain until the pension of 1813:
- 6 ème company in the 1st body of the marshal
Victor which
will become armed with Madrid then with the Centre.
- 2 ème company with the 3è body of the
general
Moncey then Suchet who will be the army of Aragon. ·
- 4 ème company with the 5th body of the major
general St
Cyr(French military academy) then Mortar which we shall call armed with
the North then with Catalonia.
- 10 ème company will arrive in 1810 with the
reinforcements
for
second armed(equipped) with Portugal of the marshal Masséna.
- Other armed forces were deprived of pontonniers, that is 2
ème
body of the general Bessière, the 4th of the general
Lefèvre and 6 ème of the general Ney 21 as well
as the
spare body. On the other hand, they could appeal to the pontonniers of
the nearby bodies
The first fights in Spain took place in the North of Spain where were
several strengthened places in which the Spanish troops had taken
refuge. It was the case to Sarragosse where the fortress resisted
triumphantly from June 29th till August 14th, 1808 to a first seat led
by the general Jean Antoine Verdier. Then the seat was abandoned, fault
of pontonniers to make cross(exceed) the river Ebre in the heavy
artillery intended to break the defences of the city.
6 ème company of
pontonniers to Espinosa

At instigation of
the
Emperor who enters personally Spain, the general Soult pushes the
Spanish troops to Burgos (in November 7th and 10th, 1808). ON THE WEST,
the general Victor, is victorious to Espinosa (in November 11th),
fights in which one(which) participated 6 ème company of
pontonniers, the first one in étre arrived on the spot. In
the
North, the general Lannes beats the Spanish troops which take refuge in
the city strengthened to Tudela (in November 23rd) while the general
Moncey pushes away(repels) the Spanish army of Aragon which take refuge
in the flat-strong of Saragossa (in November 30th).
The Emperor takes the
direction(management) of the operations
before
leaving Spain definitively.
So the Spanish armies keep(preserve) 2
bridges of important supports which threaten the lines of communication
between Madrid and Perpignan and keep(guard) the control of Ebre and
canal of Aragon which connects these two cities. The victories of
Burgos and Espinosa having dessérées the
English-Spanish
embrace, the Emperor takes with the 1st armed force the road of Madrid,
forces the parade of Somo-Sierra (in December 3rd, 1808), and returns
Joseph Napoleon in the Spanish capital on December 13th.
The general Soult, the successor of Lefèvre
commanding(ordering)
of the 2nd armed force of Spain, finishes the operation by beating on
January 19th, 1809 the troops of Wellington which went back up(raised)
of Portugal northward by the valley of Douero. In crushing defeat, the
English troops rembarquent in Corogne, in the Northwest of Spain,
abandoning their material of which a crew of bridge they
brulèrent and killed the horses which they could not embark.
Satisfied of the situation the Emperor leaves definitively Spain on
January 19th, 1809 for Bayonne then Mont-de-Marsan, He will never
return on this theatre of operation, already worried by Austria which
prepares one 5 ème coalitions. But before leaving he orders
to
take necessarily the control of the city strengthened by Saragossa
where took refuge the Spanish army of Aragon.
The war of seats 2
ème and 4 ème
companies on the
Mediterranean rib(coast)
.After the departure of the Emperor, it is king
Joseph Napoleon who took the direction(management) of the operations
and collected the workforce of two armed forces to besiege, for 2
ème time, the entrenched camp of Sarragosse.
The seat began on November 28th with 3 ème body of the
general
Moncey the sector of which was, strengthened by the infantry and the
cavalry of 6 ème body of Ney and finally 5 ème
body of
Mortar. It was necessary to wait for the arrival of park of seat and
its heavy artillery and the crew of bridge come from Bayonne with 2
ème and 4 ème companies of the 1st battalion.
Finally the
convoy which extended over more than 10 kilometres arrived by February
15th having crossed(gone through) 350 kilometres on mountainous ground.
Immediately pontonniers is put in the work and took a decisive part by
throwing(launching) with the Genius four bridges which allowed the
clearing of the river 60 details(rooms) of heavy artillery and the
infantry. It was the worst seat of the war of Spain that ended on
February 21st, 1809. He(it) cost the life to 3.100 French servicemen of
whom a majority of Polish of the regiment of the Vistula and to 54.000
civilians and Spanish soldiers.
The conquered city, 4 ème company of pontonniers and
part(party)
of the crew of bridge get back to the base of the army of the North to
Pampelune, while 2 ème company stays in Saragossa with 3
ème body which passes under command of the general Suchet.
It is the only one of four companies who will participate in the great
majority of the seats of strengthened cities or fortresses while the
other companies participated in the pitched or retired battles. She(it)
will finish the campaign of France in 1814 in Toulouse, always in the
orders of Suchet then duke of Albuféras.
During this time, the war of Spain continues and in February, 1809, the
marshal Soult penetrates again to the North of Portugal. He(it) gains a
victory in Port on March 29th but has to abandon the ground in May to
return in Spain. From this time the dissensions were daylight between
generals because new king of Spain tried(felt) difficulties being
obeyed. In fact, every commander(major) of armed force fought(disputed)
according to his appropriate(clean) interests and no action plan was
coordinated on the whole theatre of operation.
Card of the routes of the companies of pontonniers during the war of
Spain
The evolution of the
general situation, always more troops.
From 1809,
the victories and the military lapels(reverses) balance each other. The
engaged(opened) workforce was on July 1st, 1809 of 288.766 men(people)
and 36.050 horses, - according to Jean Still, in May, 2006, sources
state of situation C 8 436 SHD-. This considerable figure of troops of
activity(occupation) is going to create a strong Spanish nationalist
feeling which is going to express itself in a new war shape - the
guerrilla warfare which will cost to the imperial army more men(people)
than the fights. Indeed, the losses reached(affected) 100 men(people)
by days is some 180.000 men(people) for all the campaigns of Spain.
From their part, the insurgents, as we said until 1812, lost
approximately 25.000 men(people).
The misfortunes of the
pontonniers of the general
Eblé in
Portuga
In 1810 the status as regards military service requires
reinforcements that we made come from Germany. Among these represented
10 ème company of the 1st battalion of pontonniers arrived
with
the artillery of the army of Portugal confided(entrusted) to the
general Masséna. This army took away(gained) a series of
success. But to arrive near Torrès Vedras to the South of
Portugal where the English troops had taken refuge, it was necessary to
build for a unity of artillery of the general Tirlet a bridge of rope
which turned out effective because it supported(bore) a detail(room) of
8 with 4 horses and 2 artillerymen. It was near Punhete on the right
bank of the river Zézére. It is in this region
that
Masséna avid to facilitate its communications, asked
Eblé
his(her,its) general commanding(ordering) the artillery to
throw(launch) a bridge across the river the Tagus 23. But its 10
ème company of pontonniers was endowed only from 5 to 6
boats.
It was necessary to build on the spot about forty boats by the genius
and the pontonniers, and réquistionner or to buy so much.
Pontonniers made a lot of effort to throw(launch) this bridge which
required approximately 80 boats and was to Pinhette. But the French
troops were able to cross(exceed) the defences English which received
reinforcements by sea. The status as regards military service
deteriorated and the received general Eblé the order to
destroy(annul) this magnificent bridge which was burned on March 5th,
1811 not to be taken by the enemy. It was also necessary to
destroy(annul) 2 stealing bridges and tub, 8 nacelles and another
bridge with easel. All its bridges were destroyed(annulled) behind her,
the army was able to sound the retreat and return in Spain where it
arrived to October. Masséna will pay this lapel(reverse) by
his
disgrace and will be replaced by the general Marmont.
The defeat of Vitoria in
1813 begins the pension towards
France.
There
will not be attempt anymore to invade Portugal because the situation
deteriorates for the imperial armies on her(it) almost totality of the
Iberic peninsula, except on the Mediterranean rib(coast) held by the
army of Aragon. 10 ème company of pontonniers will follow
the
lot(fate) of three other companies and will be a part of armies of Noon
then of Andalusia and finally Pyrenees.
From the beginning of year 1812 the status as regards military service
quickly degrades in Spain, as far as workforce and numerous officers
are taken to strengthen the "Grande Armée" which gets ready
in
Germany and in Poland because Napoleon had indeed decided to open a
second forehead(front) and to invade Russia. This perspective
consolidates the English-Spanish troops which force our troops to break
the fight in Arapiles on July 22nd l812, on the road of Madrid, what
obliges king Joseph to evacuate the Spanish capital with its yard.
His(her,its) pension covered by the marshal Soult the ménera
in
Valencia, on the Mediterranean rib(coast). The army of Aragon cannot
feed this influx of servicemen and people of yard and the royal caravan
will re-hang the coastal road France. But the Spanish encerlait army
Barcelona and it was necessary to wait that she(it) is pushed
away(repelled) so that king can cross(spend) and join Pampelune then
Bayonne.
Then on October 5th the English vessels off-loaded troops and some
details(rooms) of artillery in the South of Denia but were pushed
away(repelled) by the army of Aragon. To have protected effectively the
pension of king Joseph, the marshal Soult is named(appointed) by the
Emperor to the command of the army of Spain but the imperial troops
will be beaten by the duke of Wellington on June 21st, 1813 to Vitoria.
This battle lost after the flight(leak) of king is significant and was
the signal of the general pension. Indeed, the city was the
knot
of the Pyrenean roads. And opened the road of the Basque country to the
English-Spanish and Portuguese troops. This defeat without appeal
demoralized some 197.000 men(people) still in Spain, who have only a
haste, return in France. Only Suchet resists to Tarragone with the
fragments of his(her) army of Aragon, and beats the English on June
12th, always with 2 ème company of pontoniers in its
workforce.
It is one of the last starts because on June 25th the imperial army
leaves definitively Pampelune in the direction of France, by the road
of Bayonne. The last units to leave Spain will be those of the marshal
Suchet who goes back up(raises) towards Barcelona from July 5th with
its materials and by following the Mediterranean Sea.
Grip of Bayonne by the English troops and the impact of Berezina in
Russia
On the other side, on the Atlantic facade, the English-Spanish
and Portuguese are victorious in Level November 10th whereas they take
Bayonne after a seat.
At the same time, the general Eblé commanding(ordering) 2
battalions of pontonniers saved from the destruction the "Grande
armée» in the passage of
Bérézina. This
defeat also marks the end of the Spanish theatre of operation because
on December 11th, 1813, the Emperor returns the throne of Spain to king
Ferdinand VII who belonged under house arrest to Valencay.
Of this fact and in spite of internal dissensions, the majority of the
Spanish troops get back to their country but the English troops pursue
their advance in France from Pyrenees. France weakened by the loss in
Russia of its Big-armed is now invaded on all sides.
Pontonniers in the battle
of France ( 1814 )
The battle of France
begins with fights retarding as in the battle of Orthez of January in
27 fevrier 1814 on the Atlantic quotation then in Toulouse where took
refuge the ex-army of Aragon of Suchet. But the advance of the English
troops is irresistible and on April 10th they take Toulouse. From their
part, the Prussian and Russian troops walk(work) on Paris, taking the
troops of the Emperor in pliers.
It is the beginning of the end for the campaign of France that was
going to bring Napoleon's fall.
|
xiti
|
|
modifié
30 juillet 2008 |
1-Archival Note National, put into series 384 AP 106 File Suchet.
2-2 ème company was originally allocated to 6 ème
body of
Ney but was transferred to 3 ème body of Moncey when Ney
left
Sarragosse to join king Joseph Napoleon in Madrid.
3-According to the memories(reports) of the Colorful General, the
aid-de - camp of king Joseph Napoleon ( 1775-1813 ) Paris Kolb 1893 p.
278.
4-Newspaper of the military Sciences, 2 ème put into series,
volume XXI, by J. Corréard